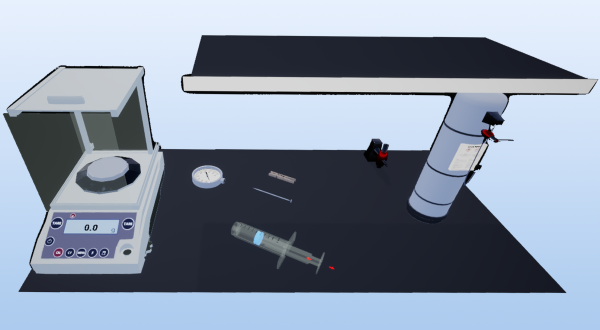
This experiment is crafted to explore the principles of physics and chemistry by determining the mass and calculating the density of an unknown gas, using propane as the subject. The process involves a series of steps including the preparation of a syringe, creating a vacuum, weighing, gas introduction, and final calculations to derive the mass and density of the gas. This methodical approach not only applies to theoretical knowledge but also hones practical skills in handling and analyzing gases.
Educational Goals
- Understanding gas properties and handling: Learn the techniques for manipulating gases, focusing on the measurement of volume and mass to explore physical properties.
- Application of theoretical principles: Directly apply principles from physics and chemistry to determine the mass and density of a gas, highlighting the practical relevance of these subjects.
- Precision in measurement: Emphasize the importance of precision in scientific measurements, encouraging meticulousness in experimental procedures.
- Skills in gas identification: Through determining the density, gain insights into methods for identifying gases, showcasing how physical properties can be leveraged for this purpose.
This experience aims to provide a comprehensive understanding of how to determine the physical properties of an unknown gas, specifically propane, through practical application. By engaging in this experiment, participants will navigate through the process of preparing the syringe, measuring vacuum, weighing, and calculating density, which illustrates the critical relationship between mass, volume, and density. This hands-on approach not only solidifies theoretical concepts in a tangible manner but also cultivates a deeper appreciation for the intricacies of scientific exploration. Through mastering the techniques of gas manipulation and analysis, participants enhance their knowledge and skills in the realms of chemistry and physics, equipped with the understanding necessary for advanced scientific inquiry.
Part A: Density determination
The objective is to calculate paraffin’s density by first measuring its mass and then determining its volume via water displacement. This process not only illustrates the concept of density but also demonstrates Archimedes’ principle in action.
Part B: Melting point measurement
This segment focuses on identifying the melting point of paraffin by preparing a sample, heating it until it transitions to a liquid state, and monitoring the temperature at which this change occurs. This exercise provides a hands-on understanding of how a substance’s melting point is determined and its significance. This two-part experience offers a comprehensive exploration of the physical properties of paraffin, providing a practical understanding of density and melting point. Through these experiments, participants not only grasp theoretical concepts in a tangible way but also hone their technical skills, from precise measurement to the critical analysis of results. This approach fosters a deeper appreciation for the nuances of material properties and their implications in scientific research and application.
Protocol
1. Push the syringe plunger to expel all the air from it.
2. Attach the plastic fitting (unknown gas canister) to the end of the syringe and close it with the clamp as close to the end as possible.
3. Pull on the plunger to create a vacuum in the syringe until reaching a volume of 95 to 100ml.
4. Lock the plunger with the nail.
5. Read the volume measurement.
6. Weigh the entire syringe-piston-fitting-nail-clamp assembly.
7. Remove the nail, clamp, and plastic fitting.
8. Push the syringe plunger to return to zero volume.
9. Attach the plastic fitting (unknown gas canister) to the end of the syringe.
10. Open the valve of the unknown gas canister.
11. Draw a volume of unknown gas equivalent to the one measured in step 4 and close the fitting with the clamp as close to the end of the syringe as possible.
12. Insert the nail into the piston hole.
13. Weigh the entire syringe, piston, fitting, clamp, and nail assembly.
Anticipated Outcomes
The 100mL syringe weighs 45g.
The nail weighs 0.5g.
The clamp weighs 0.45g.
The connector weighs 0.5g.
At step 6, the total weight is 45g + 0.5g + 0.45g + 0.5g = 46.45g.
The unknown gas is propane. Its density is 0.000493 g/mL.
A volume of 100mL of propane, at atmospheric pressure and room temperature, weighs approximately 0.0493g. This weight can thus be added to the total weight of the syringe assembly.
Significance of the experiment:
Precision in measurement: This experiment emphasizes the importance of precision in measurements, as even small weights like that of a nail or connector are considered in the total mass calculation.
Understanding gas properties: By calculating the mass of a known volume of propane, the experiment highlights how gas properties like density are crucial for identifying and understanding gases in various contexts.
Application of concepts: The experiment applies basic principles of physics and chemistry, such as mass, volume, and density, demonstrating their interplay in practical scenarios. This exercise is significant for students or practitioners in fields like chemistry, physics, and engineering, where such calculations and understanding of material properties are fundamental. It also illustrates the methodical approach needed in scientific experiments, where accuracy and attention to detail are paramount.
Summary of Assignment by Grade Range
Grades 3-5 (Ages 8-10)
- Focus: Basic introduction to gas properties and simple observations.
- Activities: Observing gas behaviour, simple demonstrations of measurements, basic safety instructions.
Grades 6-8 (Ages 11-13)
- Focus: Intermediate understanding and application of gas properties and handling techniques.
- Activities: Measuring gas volume and mass, creating a vacuum, calculating density, recording observations, following detailed safety protocols.
Grades 9-12 (Ages 14-18)
- Focus: Advanced mastery of gas properties and precise measurements.
- Activities: Detailed measurement of gas volume and mass, creating a vacuum, advanced calculations of density, detailed recording and analysis, adhering to advanced safety protocols.
Laboratory essentials
Instruments
Electronic scale
Gas tank with propane gas
Nail
Syringe
Wood clamp
Products